Resample a Vector Image#
Synopsis#
Linearly interpolate a vector image.
The Python wrapping for the LinearInterpolateImageFunction using vector images was added in ITK 4.7.0.
Results#
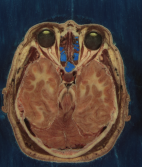
Input image#
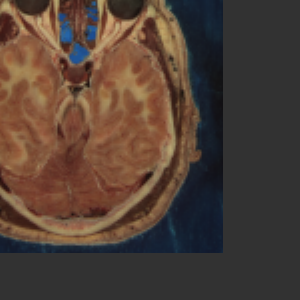
Output image#
Code#
Python#
#!/usr/bin/env python
import itk
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Resample A Vector Image.")
parser.add_argument("input_image")
parser.add_argument("output_image")
args = parser.parse_args()
PixelType = itk.RGBPixel[itk.UC]
input_image = itk.imread(args.input_image, pixel_type=PixelType)
ImageType = type(input_image)
interpolator = itk.LinearInterpolateImageFunction[ImageType, itk.D].New()
Dimension = input_image.GetImageDimension()
transform = itk.IdentityTransform[itk.D, Dimension].New()
output_image = itk.resample_image_filter(
input_image,
interpolator=interpolator,
transform=transform,
default_pixel_value=[50, 50, 50],
output_spacing=[0.5, 0.5],
output_origin=[30, 40],
size=[300, 300],
)
itk.imwrite(output_image, args.output_image)
C++#
#include "itkImageFileReader.h"
#include "itkImageFileWriter.h"
#include "itkImage.h"
#include "itkResampleImageFilter.h"
#include "itkIdentityTransform.h"
#include "itkLinearInterpolateImageFunction.h"
#include "itkRGBPixel.h"
int
main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
if (argc != 3)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << argv[0];
std::cerr << " <InputFileName> <OutputFileName>";
std::cerr << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
const char * inputFileName = argv[1];
const char * outputFileName = argv[2];
constexpr unsigned int Dimension = 2;
using PixelComponentType = unsigned char;
using PixelType = itk::RGBPixel<PixelComponentType>;
using ImageType = itk::Image<PixelType, Dimension>;
const auto input = itk::ReadImage<ImageType>(inputFileName);
using FilterType = itk::ResampleImageFilter<ImageType, ImageType>;
auto filter = FilterType::New();
using InterpolatorType = itk::LinearInterpolateImageFunction<ImageType, double>;
auto interpolator = InterpolatorType::New();
filter->SetInterpolator(interpolator);
using TransformType = itk::IdentityTransform<double, Dimension>;
auto transform = TransformType::New();
filter->SetTransform(transform);
PixelType defaultValue;
defaultValue.Fill(50);
filter->SetDefaultPixelValue(defaultValue);
ImageType::SpacingType spacing;
spacing[0] = .5; // pixel spacing in millimeters along X
spacing[1] = .5; // pixel spacing in millimeters along Y
filter->SetOutputSpacing(spacing);
ImageType::PointType origin;
origin[0] = 30.0; // X space coordinate of origin
origin[1] = 40.0; // Y space coordinate of origin
filter->SetOutputOrigin(origin);
ImageType::DirectionType direction;
direction.SetIdentity();
filter->SetOutputDirection(direction);
ImageType::SizeType size;
size[0] = 300; // number of pixels along X
size[1] = 300; // number of pixels along Y
filter->SetSize(size);
filter->SetInput(input);
try
{
itk::WriteImage(filter->GetOutput(), outputFileName);
}
catch (const itk::ExceptionObject & error)
{
std::cerr << "Error: " << error << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Classes demonstrated#
-
template<typename TInputImage, typename TOutputImage, typename TInterpolatorPrecisionType = double, typename TTransformPrecisionType = TInterpolatorPrecisionType>
class ResampleImageFilter : public itk::ImageToImageFilter<TInputImage, TOutputImage> Resample an image via a coordinate transform.
ResampleImageFilter resamples an existing image through some coordinate transform, interpolating via some image function. The class is templated over the types of the input and output images.
Note that the choice of interpolator function can be important. This function is set via SetInterpolator(). The default is LinearInterpolateImageFunction<InputImageType, TInterpolatorPrecisionType>, which is reasonable for ordinary medical images. However, some synthetic images have pixels drawn from a finite prescribed set. An example would be a mask indicating the segmentation of a brain into a small number of tissue types. For such an image, one does not want to interpolate between different pixel values, and so NearestNeighborInterpolateImageFunction< InputImageType, TCoordRep > would be a better choice.
If an sample is taken from outside the image domain, the default behavior is to use a default pixel value. If different behavior is desired, an extrapolator function can be set with SetExtrapolator().
Output information (spacing, size and direction) for the output image should be set. This information has the normal defaults of unit spacing, zero origin and identity direction. Optionally, the output information can be obtained from a reference image. If the reference image is provided and UseReferenceImage is On, then the spacing, origin and direction of the reference image will be used.
Since this filter produces an image which is a different size than its input, it needs to override several of the methods defined in ProcessObject in order to properly manage the pipeline execution model. In particular, this filter overrides ProcessObject::GenerateInputRequestedRegion() and ProcessObject::GenerateOutputInformation().
This filter is implemented as a multithreaded filter. It provides a DynamicThreadedGenerateData() method for its implementation.
- Warning
For multithreading, the TransformPoint method of the user-designated coordinate transform must be threadsafe.
- ITK Sphinx Examples:
