Compute Planar Parameterization of a Mesh#
Synopsis#
Compute planar parameterization of a surface mesh represented by one itk::QuadEdgeMesh.
Results#
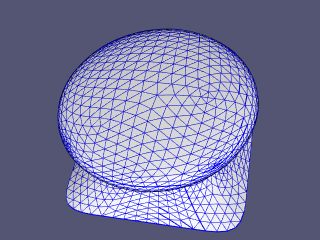
Input mesh#
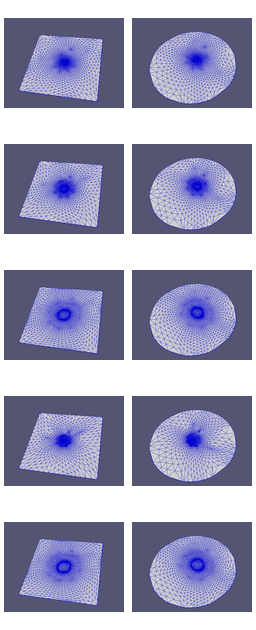
Output planes with left column) SQUARE, and right column) DISK BorderType, and row 1) OnesMatrix, 2) InverseEuclideanMatrix 3) ConformalMatrix, 4) AuthalicMatrix, and 5) HarmonicMatrix CoefficientType.#
Interactive input mesh
Interactive SQUARE BorderType, OnesMatrix CoefficientType output
Interactive DISK BorderType, OnesMatrix CoefficientType output
Code#
C++#
#include "itkQuadEdgeMesh.h"
#include "itkMeshFileReader.h"
#include "itkMeshFileWriter.h"
#include "VNLIterativeSparseSolverTraits.h"
#include "itkParameterizationQuadEdgeMeshFilter.h"
int
main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
if (argc != 5)
{
std::cout << "Requires 4 arguments: " << std::endl;
std::cout << "1-Input file name " << std::endl;
std::cout << "2-Border Type" << std::endl;
std::cout << " * 0: SQUARE" << std::endl;
std::cout << " * 1: DISK" << std::endl;
std::cout << "3-CoefficientType Type" << std::endl;
std::cout << " * 0: OnesMatrixCoefficients" << std::endl;
std::cout << " * 1: InverseEuclideanDistanceMatrixCoefficients" << std::endl;
std::cout << " * 2: ConformalMatrixCoefficients" << std::endl;
std::cout << " * 3: AuthalicMatrixCoefficients" << std::endl;
std::cout << " * 4: HarmonicMatrixCoefficients" << std::endl;
std::cout << "4-Output file name " << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
const char * inputFileName = argv[1];
const char * outputFileName = argv[4];
using CoordType = double;
constexpr unsigned int Dimension = 3;
using MeshType = itk::QuadEdgeMesh<CoordType, Dimension>;
using ReaderType = itk::MeshFileReader<MeshType>;
using WriterType = itk::MeshFileWriter<MeshType>;
using BorderTransformType = itk::BorderQuadEdgeMeshFilter<MeshType, MeshType>;
using SolverTraits = VNLIterativeSparseSolverTraits<CoordType>;
using ParametrizationType = itk::ParameterizationQuadEdgeMeshFilter<MeshType, MeshType, SolverTraits>;
auto reader = ReaderType::New();
reader->SetFileName(inputFileName);
MeshType::Pointer mesh = reader->GetOutput();
auto border_transform = BorderTransformType::New();
border_transform->SetInput(reader->GetOutput());
int border;
std::stringstream ssout(argv[2]);
ssout >> border;
switch (border) // choose border type
{
case 0: // square shaped domain
border_transform->SetTransformType(itk::BorderQuadEdgeMeshFilterEnums::BorderTransform::SQUARE_BORDER_TRANSFORM);
break;
case 1: // disk shaped domain
border_transform->SetTransformType(itk::BorderQuadEdgeMeshFilterEnums::BorderTransform::DISK_BORDER_TRANSFORM);
break;
default: // handle .... user ....
std::cerr << "2nd argument must be " << std::endl;
std::cerr << "0 for SQUARE BORDER TRANSFORM or "
<< "1 for DISK BORDER TRANSFORM" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
std::cout << "Transform type is: " << border_transform->GetTransformType() << std::endl;
// ** CHOOSE AND SET BARYCENTRIC WEIGHTS **
itk::OnesMatrixCoefficients<MeshType> coeff0;
itk::InverseEuclideanDistanceMatrixCoefficients<MeshType> coeff1;
itk::ConformalMatrixCoefficients<MeshType> coeff2;
itk::AuthalicMatrixCoefficients<MeshType> coeff3;
itk::HarmonicMatrixCoefficients<MeshType> coeff4;
auto param = ParametrizationType::New();
param->SetInput(mesh);
param->SetBorderTransform(border_transform);
int param_type;
std::stringstream ssout3(argv[3]);
ssout3 >> param_type;
switch (param_type)
{
case 0:
param->SetCoefficientsMethod(&coeff0);
break;
case 1:
param->SetCoefficientsMethod(&coeff1);
break;
case 2:
param->SetCoefficientsMethod(&coeff2);
break;
case 3:
param->SetCoefficientsMethod(&coeff3);
break;
case 4:
param->SetCoefficientsMethod(&coeff4);
break;
default:
std::cerr << "3rd argument must be " << std::endl;
std::cerr << "0, 1, 2, 3 or 4" << std::endl;
std::cerr << "Here it is: " << param_type << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
auto writer = WriterType::New();
writer->SetInput(param->GetOutput());
writer->SetFileName(outputFileName);
try
{
writer->Update();
}
catch (const itk::ExceptionObject & error)
{
std::cerr << "Error: " << error << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Classes demonstrated#
-
template<typename TInputMesh, typename TOutputMesh, typename TSolverTraits>
class ParameterizationQuadEdgeMeshFilter : public itk::QuadEdgeMeshToQuadEdgeMeshFilter<TInputMesh, TOutputMesh> Compute a planar parameterization of the input mesh.
This filter computes a mapping in between a planar parametric domain and one input mesh.
This filter is made for fixed boundary parameterization where the parametric domain shape is given by the means of the border transform. Then, the position of internal vertices (not on the boundary) is directly connected to m_CoefficientsComputation.
This filter internally creates and solves a sparse linear system: storage and computation can be set by the means of TSolverTraits. Since for 3D meshes, this filter solves for similar sparse linear systems for the three dimensions, it is highly recommended to use one direct solver which would first decompose sparse matrix (e.g. VNLSparseLUSolverTraits).
This implementation was taken from the Insight Journal paper: https://www.insight-journal.org/browse/publication/202
- ITK Sphinx Examples:
