Run Image Filter on Region of Image#
Synopsis#
Run an image filter on a region of an image.
Results#
Input image#
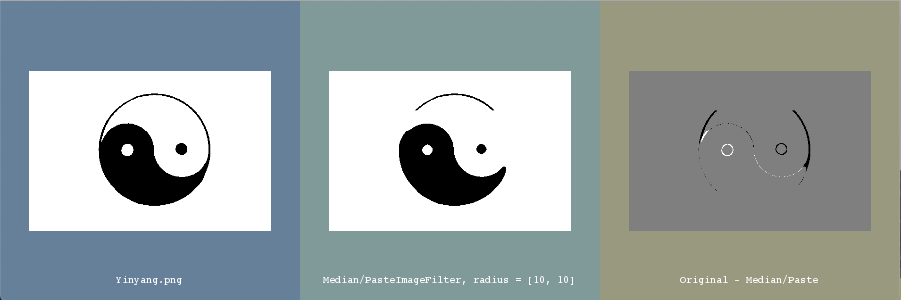
Output In VTK Window#
Code#
C++#
#include "itkImage.h"
#include "itkImageFileReader.h"
#include "itkMedianImageFilter.h"
#include "itkPasteImageFilter.h"
#include "itkSubtractImageFilter.h"
#include "itksys/SystemTools.hxx"
#include <sstream>
#ifdef ENABLE_QUICKVIEW
# include "QuickView.h"
#endif
int
main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
// Verify command line arguments
if (argc < 2)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << argv[0] << " InputImageFile [radius]" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
std::string inputFileName = argv[1];
// Setup types
using ImageType = itk::Image<float, 2>;
using FilterType = itk::MedianImageFilter<ImageType, ImageType>;
using SubtractType = itk::SubtractImageFilter<ImageType>;
using PasteType = itk::PasteImageFilter<ImageType, ImageType>;
const auto input = itk::ReadImage<ImageType>(inputFileName);
// Create and setup a median filter
auto medianFilter = FilterType::New();
FilterType::InputSizeType radius;
radius.Fill(2);
if (argc > 2)
{
radius.Fill(atoi(argv[2]));
}
itk::Size<2> processSize;
processSize[0] = input->GetLargestPossibleRegion().GetSize()[0] / 2;
processSize[1] = input->GetLargestPossibleRegion().GetSize()[1] / 2;
itk::Index<2> processIndex;
processIndex[0] = processSize[0] / 2;
processIndex[1] = processSize[1] / 2;
itk::ImageRegion<2> processRegion(processIndex, processSize);
medianFilter->SetRadius(radius);
medianFilter->SetInput(input);
medianFilter->GetOutput()->SetRequestedRegion(processRegion);
auto pasteFilter = PasteType::New();
pasteFilter->SetSourceImage(medianFilter->GetOutput());
pasteFilter->SetSourceRegion(medianFilter->GetOutput()->GetRequestedRegion());
pasteFilter->SetDestinationImage(input);
pasteFilter->SetDestinationIndex(processIndex);
auto diff = SubtractType::New();
diff->SetInput1(input);
diff->SetInput2(pasteFilter->GetOutput());
#ifdef ENABLE_QUICKVIEW
QuickView viewer;
viewer.AddImage(input.GetPointer(), true, itksys::SystemTools::GetFilenameName(inputFileName));
std::stringstream desc;
desc << "Median/PasteImageFilter, radius = " << radius;
viewer.AddImage(pasteFilter->GetOutput(), true, desc.str());
std::stringstream desc2;
desc2 << "Original - Median/Paste";
viewer.AddImage(diff->GetOutput(), true, desc2.str());
viewer.Visualize();
#endif
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Classes demonstrated#
-
template<typename TInputImage, typename TSourceImage = TInputImage, typename TOutputImage = TInputImage>
class PasteImageFilter : public itk::InPlaceImageFilter<TInputImage, TOutputImage> Paste an image (or a constant value) into another image.
PasteImageFilter allows a region in a destination image to be filled with a source image or a constant pixel value. The SetDestinationIndex() method prescribes where in the destination input to start pasting data from the source input. The SetSourceRegion method prescribes the section of the second image to paste into the first. When a constant pixel value is set, the SourceRegion describes the size of the region filled. If the output requested region does not include the SourceRegion after it has been repositioned to DestinationIndex, then the output will just be a copy of the input.
This filter supports running “InPlace” to efficiently reuse the destination image buffer for the output, removing the need to copy the destination pixels to the output.
When the source image has a lower dimension than the destination image then the DestinationSkipAxes parameter specifies which axes in the destination image are set to 1 when copying the region or filling with a constant.
The two inputs and output image will have the same pixel type.
- ITK Sphinx Examples:
