Use ParallelizeImageRegion#
Synopsis#
This example demonstrates how to use MultiThreaderBase::ParallelizeImageRegion to apply a non-trivial operation for all pixels in an image, in parallel. To perform a multi-threaded operation like this prior ITK 5.0 required the creation of a class.
Results#
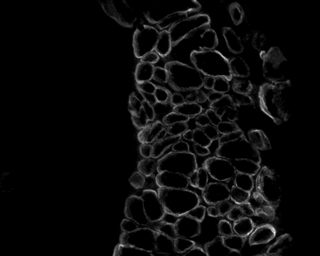
Segmentation and custom colorization of an image using MultiThreaderBase::ParallelizeImageRegion.#
Code#
C++#
#include "itkImageFileReader.h"
#include "itkImageFileWriter.h"
#include "itkWatershedImageFilter.h"
#include "itkImageRegionIterator.h"
constexpr unsigned int Dimension = 2;
using InputPixelType = unsigned char;
using InputImageType = itk::Image<InputPixelType, Dimension>;
using OutputPixelType = itk::RGBAPixel<unsigned char>;
using OutputImageType = itk::Image<OutputPixelType, Dimension>;
using LabeledImageType = itk::Image<itk::IdentifierType, Dimension>;
OutputImageType::Pointer
segmentationAndCustomColorization(InputImageType::Pointer inImage)
{
using WatershedFilterType = itk::WatershedImageFilter<InputImageType>;
auto watershed = WatershedFilterType::New();
watershed->SetThreshold(0.05);
watershed->SetLevel(0.3);
watershed->SetInput(inImage);
watershed->Update();
LabeledImageType::Pointer image = watershed->GetOutput();
image->DisconnectPipeline();
auto outImage = OutputImageType::New();
outImage->CopyInformation(image);
outImage->SetRegions(image->GetBufferedRegion());
outImage->Allocate(true);
itk::MultiThreaderBase::Pointer mt = itk::MultiThreaderBase::New();
// ParallelizeImageRegion invokes the provided lambda function in parallel
// each invocation will contain a piece of the overall region
mt->ParallelizeImageRegion<Dimension>(
image->GetBufferedRegion(),
// the lambda will have access to outer variables 'image' and 'outImage'
// it will have parameter 'region', which needs to be processed
[image, outImage](const LabeledImageType::RegionType & region) {
itk::ImageRegionConstIterator<LabeledImageType> iIt(image, region);
itk::ImageRegionIterator<OutputImageType> oIt(outImage, region);
for (; !iIt.IsAtEnd(); ++iIt, ++oIt)
{
LabeledImageType::IndexType ind = iIt.GetIndex();
OutputPixelType p;
p.SetAlpha(iIt.Get());
static_assert(Dimension <= 3, "Dimension has to be 2 or 3");
for (unsigned d = 0; d < Dimension; ++d)
{
p.SetElement(d, ind[d]);
}
oIt.Set(p);
}
},
nullptr); // we don't have a filter whose progress needs to be updated
return outImage;
}
int
main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
if (argc != 3)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << argv[0];
std::cerr << " <InputFileName>";
std::cerr << " <OutputFileName>" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
const auto input = itk::ReadImage<InputImageType>(argv[1]);
try
{
OutputImageType::Pointer outImage = segmentationAndCustomColorization(input);
itk::WriteImage(outImage, argv[2], true); // compression
}
catch (const itk::ExceptionObject & error)
{
std::cerr << "Error: " << error << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Classes demonstrated#
-
class MultiThreaderBase : public itk::Object
A class for performing multithreaded execution.
Multithreaders are a class hierarchy that provides support for multithreaded execution by abstracting away platform-specific details. This class can be used to execute a single method on multiple threads or to parallelize an operation over a given image region or array.
Subclassed by itk::PoolMultiThreader, itk::TBBMultiThreader
